General - Arthritis
Arthritis
What is arthritis?
The term arthritis literally means inflammation of a joint, but is generally used to describe any condition in which there is joint swelling and pain. Inflammation is the body's natural response to injury; the signs of inflammation being present are redness, swelling, heat and pain. It can affect any synovial joint in the body; the hip and knee joint are the most commonly affected by arthritis.
The lining of joints is cartilage (Hyaline cartilage). It coats the ends of bone in a joint and is able to absorb loads and stresses. It has a very low coefficient of friction - to allow smooth movement of the joint.
The amount of cartilage damage, synovial lining inflammation and swelling of the joint varies with the type and stage of the arthritis. Usually the early pain is due to inflammation. Later in the disease, pain is from the irritation of the worn joint structures - and inability of the joint to move properly and smoothly
What are the different types of arthritis?
There are many different types of arthritis the most common ones being Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. It can affect all age groups and children can also be affected with inflammatory arthritis.
Osteoarthritis
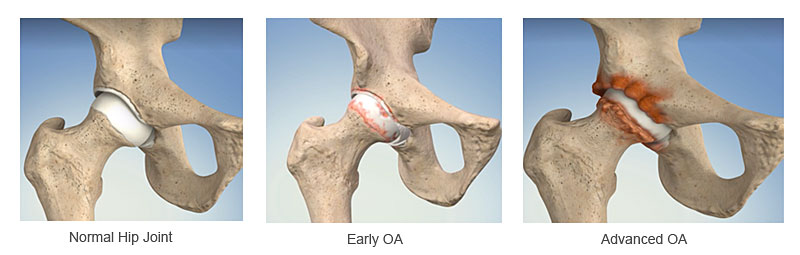
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis. It is often referred to as wear and tear arthritis as it involves the thinning and breakdown of the articular cartilage lining of the joint. The bone may lose shape and thicken at the ends or produce bony spurs (osteophytes). It causes pain in the joints and surrounding soft tissues and limits the range of movement of a joint.
Osteoarthritis affects many joints including the large, weight bearing joints of the body, the hips and knees and also the spine, hands, feet and shoulders. There are several reasons for the development of osteoarthritis including age, being overweight, heredity factors, and joint damage from a previous injury or during early development of a joint. The severe pain of osteoarthritis can be very tiring and disabling.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system (the body's way of fighting infection) attacks healthy joints, tissues, and organs. Occurring most often in women of childbearing age, this disease inflames the synovial lining of the joints. It can cause pain, stiffness, swelling, and loss of function in joints. When severe, rheumatoid arthritis can cause deformity of the joints leading to disability and loss of function.
Rheumatoid arthritis affects most commonly the joints of the hands and feet and tends to be symmetrical (affecting both sides of the body).
RA is two to three times more common in women than in men. Today modern drugs are able to control the disease process and maintain joint function, thereby reducing the need for joint replacement surgery.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis describes a form of arthritis that mainly affects the joints of the spine particularly cervical spine (the neck). However it may affect other parts of the body, e.g. hips, shoulders, knees or ankles. It causes inflammation outside the joint where the ligaments and tendons are attached to the bone, whereas in most forms of arthritis the inside of the joint is inflamed.
It usually affects the small joints between the vertebrae of the spine reducing the movements, which take place at these joints. It affects younger people, teenagers to mid thirties and more men than women.
What causes arthritis?
Predisposing factors to Osteoarthritis include age, gender, race and genetics all of which we cannot alter.
Potentially preventable predisposing factors include: Being overweight, Injury, and joint trauma - Trauma in the hip and knee from fractures, torn ligaments, cartilage (menisci) and femoro acetabular impingement (see FAI)
Mechanical stresses on the joints are increased, due to deformity and misalignment - accelerating wearing away of the articular cartilage.
What are the symptoms of arthritis?
Symptoms vary according to the type of arthritis. Each type of arthritis affects the body differently. Arthritic symptoms generally include:
• Pain and swelling or tenderness in one or more joints
• There can be redness and warmth in the joint
• Stiffness and limitation of motion of the joint
• Stiffness of the joint with inactivity and in the morning
• Skin changes and rashes.
• Overall as the disease progresses there is reduction of activity and function with loss of quality of life despite conservative treatment.
How can arthritis be managed?
Initially conservative measure are utilised to help with the pain and disability which include:
• Education and understanding of the disease and its progress
• Activity level and lifestyle can be modification
• Weight loss reduces load on the joint and can improve symptoms
• Diet, foods rich in Omega-3, Turmeric may reduce inflammation and the symptoms of arthritis.
• Physical therapy and regular non-impact exercise.
• Using a walking stick in the opposite hand
• Simple painkillers, anti–inflammatory medication and supplements can be of help if tolerated.
• Joint injections with a steroid and local anaesthetic and /or Hyaluronic acid (viscosimeters) an artificial synovial fluid. Some of the injections are carried out under X ray control. If these injection help they can be repeated.
Studies have shown that regular exercise helps people with arthritis by reducing joint pain and stiffness and increasing flexibility, muscle strength and energy. It also helps with weight reduction and offers an improved sense of well-being.
Exercise in heated swimming pools-hydrotherapy can bring enormous relief from pain and stiffness in the joints.
Mr Aslam Mohammed Consultant Hip and Knee Surgeon